Renewable energy has created a "gold rush" in this depressed environment in Germany, giving a hospice jobs either in the country and a great promise.
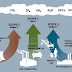
Natural resources that attract investors and industry is a black simple: wind, solar, agricultural products and agricultural waste such as liquid fertilizers.
The rush to exploit the resources in the green state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania is reminiscent of the madness that accompanies the discovery of gold or oil in the last centuries. The rumor is felt in the cities and shiny new facilities in the entire Baltic coast of the state.
"Renewable energy has become extremely valuable to our state," said the prime minister, Erwin sale, in an interview with Reuters "is a great opportunity -. Renewable energy and create manufacturing jobs.
"Point of view of design, we were one of the weakest areas of Germany, but the country is abandoning nuclear power only works if there is an equivalent and significantly -.. -.. To increase sources of renewable energy will be one of Germany's most important sectors in the future we want to be there in the middle. "
The federal government has done a U-turn on nuclear power after the accident, Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan, set off by the earthquake and tsunami of March 11. Germany, closed its eight nuclear power plants, and closes the other nine by 2022.
Germany is a world leader in renewable energy and want an even larger share of the market 211 000 000 000 dollars worldwide. One-fifth of its electricity comes from renewable sources, up from 6 percent in 2000 and aims to increase this share to 35 percent in 2020.
There are some clouds on the horizon. State mandated incentives that have fueled a boom in private investment, have been cut, pushing margins in sectors such as solar energy.
Moreover, delays in the expansion and strengthening of the national high voltage transmission lines in sparsely populated coastal areas, such as in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, in areas where the power required to the west and the south.
The federal government is working to remove bottlenecks, but if the network is not developed as soon as it can cause problems later when the offshore wind passes over online.
BUILDING Eclipse variable
Renewable energy - wind energy in particular - is injected new optimism in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, which translates into a word that appears often in conversations with business and political leaders "Reindustrialisierung" (re-industrialization).
In a state with a maritime heritage, there are now more jobs in renewable energy in construction sites: 6,000 jobs in 704 companies are expected to quadruple to nearly 22,000 in 2020.
Businesses include construction, design, maintenance and operation of wind turbines and photovoltaic and biomass power plants - where farmers grow crops and animal waste collection. There are more than 1,200 wind turbines on land, and a new start in offshore wind in the Baltic Sea will further fuel this growth.
Many of the new jobs in companies such as Nordex, which employs 1000 in Rostock to make a light rotor blades of wind turbines up to 65 meters in length. It has invested 100 million euros to expand facilities and exports about 95 percent of its production.
It is absolutely necessary, highly skilled jobs in a sparsely populated state whose industrial base was devastated by the economic upheaval following the reunification of Germany in 1990. There were 32,800 jobs in the shipyards busy time around the port city of Rostock, when the Berlin Wall fell in 1989.
But most were dashed when the German shipbuilding industry collapsed East in light of the costs of labor and rising competition tough West. There are only 3300 construction jobs back, and the collapse of the industry decline is embodied.
Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania has become one of the poorest regions of Germany. Unemployment has risen 20 percent in 2004 - twice the national average - and the population fell by 250,000 to 1.6 million mostly young, educated people moved to more prosperous west in search of jobs. More than 8,000 left the state in 2008 but only moved to 3500 in 2010.
The prospect that some regions may become ghost towns was an explosive issue, but obscurity is promising that unemployment was reduced by almost half. The state with the worst unemployment rate in Germany 16 states in 2007 is now in front of Berlin and Bremen.
"There's a new sense of optimism with sectors such as renewable energy, and the westward migration, slowing, if not completely stopped," says Guenther, a professor of environmental management at the University Dresden Technical.
The POWER of the exporting State
Juergen Trittin, the Green leader in Berlin, said a law written by renewables in 2000 that his party has proved an unexpected success in creating jobs everywhere to the east.
"All the benefits is that" he said. "Employment growth will continue to grow in the off-shore."
Germany first commercial offshore wind farm, the "Baltic 1" - 48 million of the project, where 21 wind turbines from Siemens and EnBW to maintain - it started to pump enough power for 53,000 displaced families in the network May 16 kilometers north of the coast.
By 2013, the utility EnBW aims to complete more than 80 off-shore "2-D Sea, 32 km offshore.
Germany expects to have about 25 megawatts of offshore wind capacity in 2030, 4000 produced by wind turbines.
Mecklenburg-West Pomerania, already receives half of its electricity from renewable sources - almost 4 GWh. This is a fivefold increase since 2000.
It aims to cover all its electricity needs from 2015 to 2017, then export surpluses to other States. In 2020, expect to have 12 hours of energy renewable gigawatts - enough for 3 million households. Mecklenburg-Vorpommern then produce enough power for himself and two neighboring states.
"Natural conditions for renewable energy is good here," said Sell call. "The first goal is to cover our own electricity needs. So we want to be a state energy exporter."

0 comments:
Post a Comment